Below you'll find information about accessing and using the analysis tools. This information applies to all standard feature analysis tools.
Note:
This topic discusses the standard feature analysis tools available in the portal. For information about the GeoAnalytics Tools, see Perform analysis using ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server. See Understanding analysis in ArcGIS Enterprise for an overview of each toolset.
License:
The administrator of your organization needs to grant you certain privileges for you to perform analysis. To use any of the analysis tools, you need the following privileges:
- Create, update, and delete content
- Publish hosted feature layers
- Standard Feature Analysis
If you do not have these privileges, you will not see the Perform Analysis option as described below.
Certain tools need additional privileges such as Network Analysis and GeoEnrichment. See Perform analysis for more information about these tools.
Access the tools
To access and use analysis tools in Map Viewer, follow these steps:
- Open a web map containing the feature layer or layers you want to analyze in Map Viewer.
- Click the Contents button in the Details pane.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Analysis button
 on the map menu bar.
on the map menu bar. - Hover over the layer you want to analyze and click the Analysis button
 .
.
- Click the Analysis button
Both actions open the Perform Analysis pane.
Explore the Feature Analysis pane
The Feature Analysis pane is illustrated below. This pane contains a number of categories and each category contains tools. To view the tools within a category, click the expand or collapse button on the left side of the category.
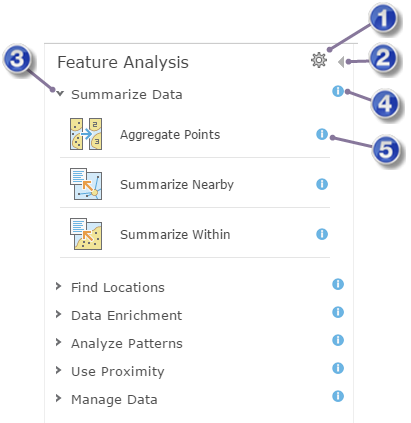
 | Open the Analysis Environments dialog box. |
 | Return to the Details pane. |
 | Expand the category to view the tools it contains. |
 | View help about the category. |
 | View help for the tool. |
Note:
Analysis environments are now available in the ArcGIS Enterprise portal to allow for GeoAnalytics Tools and raster analysis but can be used for standard tools as well. Processing Extent is the only environment that is used by standard tools. However, more environments will appear in the Analysis Environments pane if GeoAnalytics Tools and raster analysis are enabled in your portal.
Work with a tool pane
To open an analysis tool pane, click the tool icon. This opens the tool's pane as illustrated below with the Aggregate Points tool.
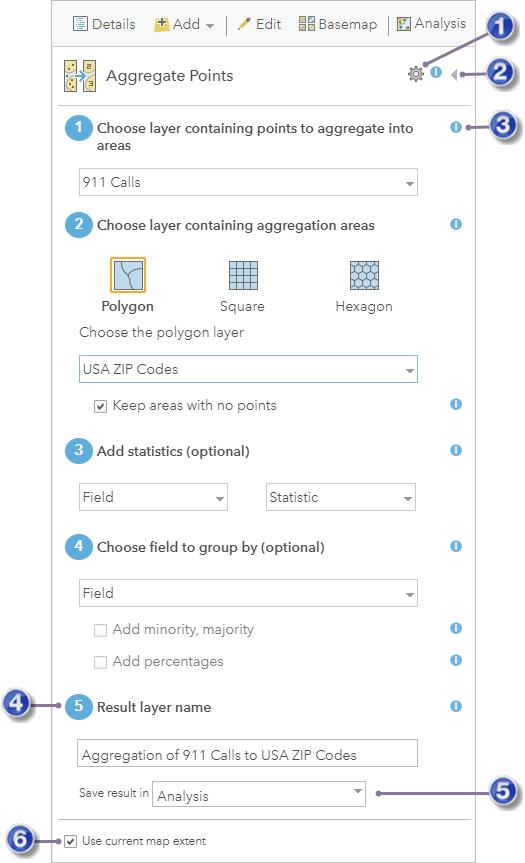
 | Open the Analysis Environments dialog box for the tool. |
 | Close the tool pane without running the analysis and return to the Perform Analysis pane. |
 | Get help about a parameter. |
 | The result of running the analysis is saved to Content using this name. |
 | You can specify a folder in Content in which to save the result. |
 | If checked, only the data visible in the current map will be analyzed. |
Note:
Analysis environments can be set from the tool pane. Processing Extent is the only environment that is used by the standard tools. The Processing Extent setting applies to all tools, even when the extent is set in a tool pane. The Use current map extent parameter will be unchecked when Processing Extent is set. Checking Use current map extent will override Processing Extent.
Each tool has a different set of parameters. You can always view help for a parameter by clicking the help icon next to the parameter as illustrated above. All tools have a Result layer name parameter where the results of running the analysis are written. You can change this name or use the default value.
Use current map extent
It is recommended that you always check Use current map extent and that you zoom in to the area you want analyzed. Doing so limits the number of features the tool needs to examine when performing analysis. It also limits the number of credits that may be used by the tool if it is configured to use utility services from ArcGIS Online. If you uncheck Use current map extent, all features in the analysis layer will potentially be analyzed, and ArcGIS Online credits used by the tool will be based on the number of features in the layer.
Rerun analysis tools
Analysis tools can be rerun by clicking the Rerun Analysis button  for a result layer. Rerun Analysis will open the tool that was used to create the layer and repopulate all of the parameters. The tool can be rerun with the same parameters, or the parameters, including inputs, can be updated before the tool is run.
for a result layer. Rerun Analysis will open the tool that was used to create the layer and repopulate all of the parameters. The tool can be rerun with the same parameters, or the parameters, including inputs, can be updated before the tool is run.
When rerunning analysis tools, the state of the current map will be honored, including filters, extent, input layers, and output folder. If you want to ensure that an analysis is rerun at a specific extent, create a bookmark. If you share your results with the intention of allowing other users to rerun your analysis, you may need to share your input layers as well. If you open a tool using Rerun Analysis and the input layers are not available, a warning will be displayed but the tool can still be run with different inputs.
Note:
The Result layer name from the previous iteration will be used when you open an analysis tool using Rerun Analysis. You must create a unique name before rerunning a tool.
Layers and data you can analyze
Note:
Some tools only work on certain kinds of feature types; for example, Aggregate Points requires an input layer containing point features.
You have the following options when choosing a layer to analyze:
- Choose a layer from your map.
- Use Choose Analysis Layer to view and select any layer in the portal to which you have access, including feature layers from your content or shared with you, or Living Atlas Analysis Layers.
Some complex datasets from ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World are not supported for Enrich Layer. An equivalent Living Atlas Analysis Layer should be used instead of a complex layer.
Tip:
Use an asterisk (*) as a wild card when searching for content in the Choose Analysis Layer window. For example, if you are looking for layers with Australia in their title, search for Aus*.You can perform analysis on the following types of layers and data:
- Feature
service
The portal must be able to access the feature service; therefore, the URL to the service must either be publically accessible or within the same network as the portal and hosting server you use to run the analysis. You cannot perform analysis on layers based on nonaccessible feature services.
ArcGIS Server feature services you add to your portal must contain fewer than 100,000 features to be used in analysis. As the complexity of the features in the service increases, the number of features you can analyze decreases. For example, if the service contains polygon features that have thousands of vertices each, you might only be able to analyze a few hundred features. If the number or complexity of features exceeds what the tool can support, you will receive an error message.
- Map service
As with feature services, the map service must be publically accessible or within the same network as the analyzing portal and hosting server.
- Hosted feature layers
- Hosted WFS layers
- Hosted tile layers
The layer must have the query capability enabled.
- Comma-separated values (CSV) file (.csv)
- KML layers
- GPS exchange format file (.gpx)
- Shapefile (.zip)
- GeoRSS web feed
- Map notes
- Route layers
- WFS layers
- Table layers
Note:
You are unable to perform analysis on layers outside of your organization that use web-tier authentication.
Analysis output
Most analysis tools that are run in Map Viewer create hosted feature layers as output. These output layers are projected in the spatial reference of the input layer.